Natural Farming
SWOT analysis of NF
Strengths
- Providing wonderful solutions to the challenges of present agriculture in the state
- Potential to contribute to the global effort to overcome the challenges of climate change
- Improving profitability in agriculture
- Improving farmers’ health
- Reducing farmers’ stress
Opportunities
- Growing demand for chemical free food
- International support for the mitigation and adaption of the climate change
Weakness
- Not able to reach the needy
- Not able to command the commensurate prices
- Less awareness and inadequate extension services
- Non-availability of readymade biological inputs at the time of requirement.
- No improvement in biological inputs formulations
Threats
- The programme is going against the powerful mainstream industries, institutions and policies
Objectives of NF
- Ensuring food security and producing more with less resources.
- For building the resilience of smallholder farmers for creating a food-secure future.
- NF is the right solution to fight climate change and create resilient food systems.
- Fighting drought is one of the main objectives of NF.
- The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the UN advocates environmentally-friendly farming methods that can take us to a more sustainable future.
- Importance for chemical free food consumption is growing rapidly.
- Chemical farming has made food a poison and also has reduced the yield by making lands barren.
- Farmers’ welfare and sustainable practices are vital for a sustainable and productive economy.
- NF constitutes an effective strategy for achieving SDGs targets.
Features of NF
- It is a farming practice that believes in natural growth of crops without adding any chemical fertilizers and pesticides.
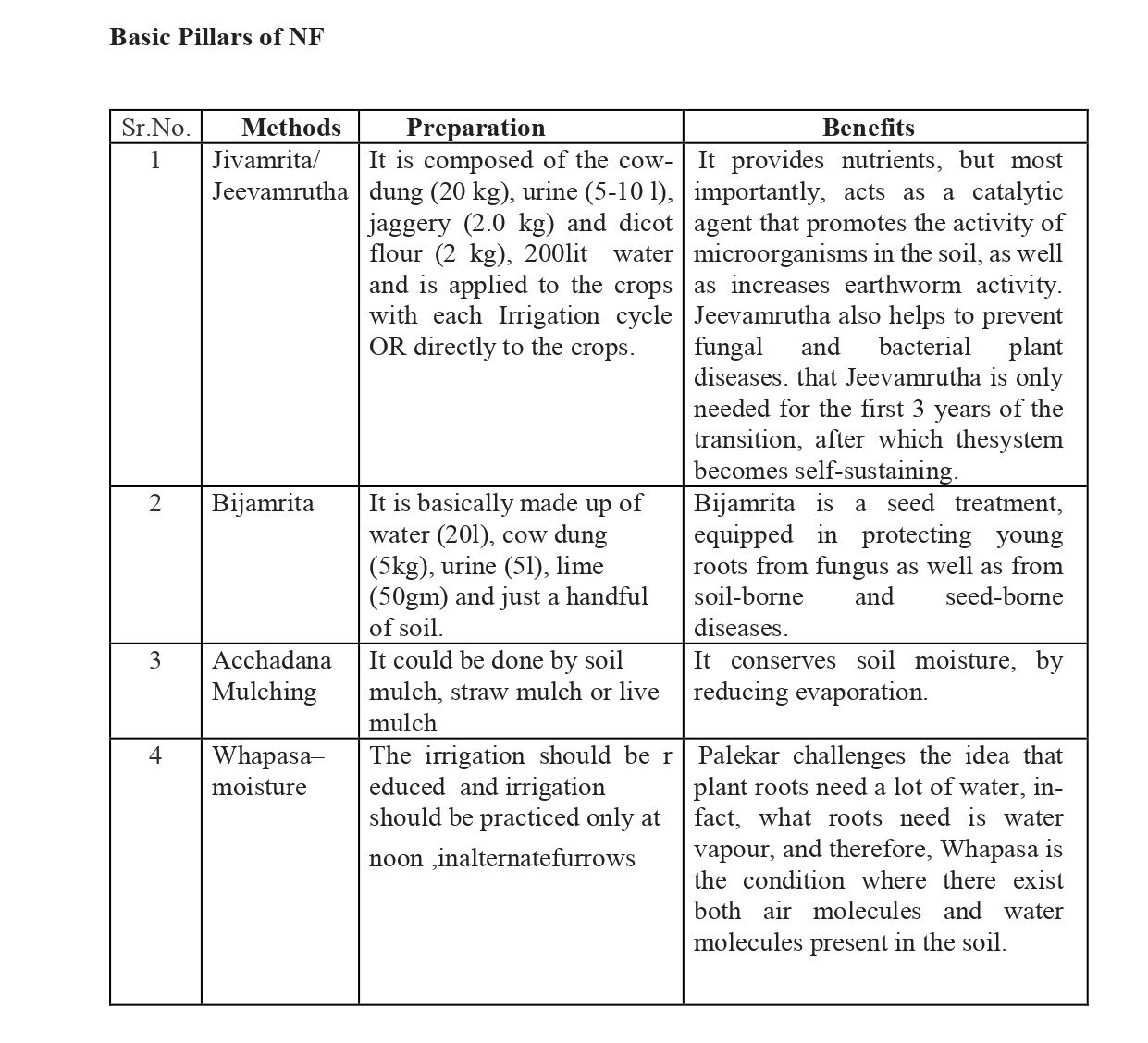
- The four wheels of NF are Bijamrut, Jivamrut, Mulching and Waaphasa.
- Bijamrut is a natural way of seed treatment using local cow urine and cow dung.
- Jvamrut is made using water, local cow dung, local cow urine, jaggery, dal flour and soil.
- Waaphasa is the aeration in the soil.
- NF is different from organic farming.
- Intercropping is an important feature of NF.
- Practicing composting on the farm itself, so that soil organic matter increases.
- Storing water in the farm ponds for use in adverse conditions.
- Insects and pests are managed using neem leaves, neem pulp and green chillies.
- Establishing farmers’ federations and self-help groups, and placing farmers at the forefront of knowledge creation and dissemination.
Advantages
- Besides reduced input cost, farmers practicing NF gets higher yields.
- Elimination of chemical pesticides and promotion of good agronomic practices.
- Promote regenerative agriculture, improve soil biodiversity and productivity.
- Ensure decent livelihoods to smallholder farmers.
- Restore ecosystem health through diverse, multi-layered cropping systems.
- Anyone who is having half an acre of land can start NF.
- Using NF techniques, one can convert even the most infertile land into a fertile one.
- Women’s empowerment and nutrition.